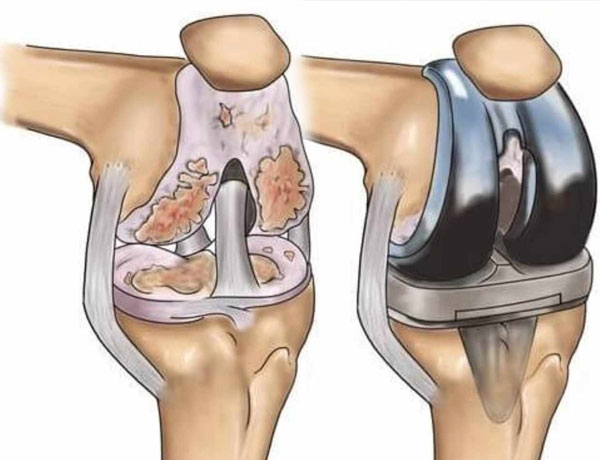
Knee Replacement
Knee replacement, also called knee arthroplasty or total knee replacement, is a surgical procedure to resurface a knee damaged by arthritis. Metal and plastic parts are used to cap the ends of the bones that form the knee joint, along with the kneecap. This surgery may be considered for someone who has severe arthritis or a severe knee injury.
Various types of arthritis may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects mostly middle-aged and older adults, may cause the breakdown of joint cartilage and adjacent bone in the knees. Rheumatoid arthritis, which causes inflammation of the synovial membrane and results in excessive synovial fluid, can lead to pain and stiffness. Traumatic arthritis, arthritis due to injury, may cause damage to the cartilage of the knee.
The goal of knee replacement surgery is to resurface parts of the knee joint that have been damaged and to relieve knee pain that cannot be controlled by other treatments.
Why it's done
The most common reason for knee replacement surgery is to relieve severe pain caused by osteoarthritis. People who need knee replacement surgery usually have problems walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs. Some also have knee pain at rest.
Risks
Knee replacement surgery, like any surgery, carries risks. They include:
- Infection
- Blood clots in the leg vein or lungs
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Nerve damage
Signs of infection
Notify your doctor immediately if you notice:
- Fever greater than 100 F (37.8 C)
- Shaking chills
- Drainage from the surgical site
- Increasing redness, tenderness, swelling and pain in the knee
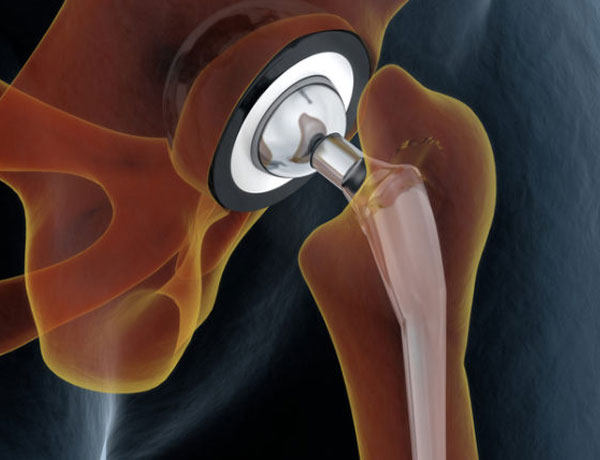
Hip Replacement
What is hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement is the removal and replacement of portions of the pelvis and femur (thighbone) that form your hip joint. It is performed primarily to relieve hip pain and stiffness caused by hip arthritis.
This procedure is also sometimes used to treat injuries such as a broken or improperly growing hip, and for other conditions.
How do you know if you need a hip replacement?
If you have these arthritis symptoms, you should consider a hip replacement:
- Severe hip pain that is not relieved by medication and that interferes with your work, sleep or everyday activity.
- Hip stiffness that restricts motion and makes it difficult to walk
What are the different types of hip replacement surgery?
The three major types of hip replacement are:
- total hip replacement (most common)
- partial hip replacement
- hip resurfacing
The most common type of hip replacement surgery is called total hip replacement (also called total hip arthroplasty). In this surgery, worn-out or damaged sections of your hip are replaced with artificial implants. The socket is replaced with a durable plastic cup, which may or may not also include a titanium metal shell. Your femoral head will be removed and replaced with a ball made from ceramic or a metal alloy. The new ball is attached to a metal stem that is inserted into the top of your femur.
Two other types of hip replacement surgeries are each generally appropriate for patients of specific age groups and activity levels:
- Partial hip replacement (also called hemiarthroplasty) involves replacing only one side of the hip joint – the femoral head – instead of both sides as in total hip replacement. This procedure is most commonly done in older patients who have fractured their hip.
- Hip resurfacing of the femoral head and socket is most commonly done in younger, active patients.
Hip replacement surgical methods
There are two major surgical approach methods for performing a total hip replacement:
- the posterior approach (more common)
- the anterior approach (sometimes called the "mini-anterior approach" or "muscle-sparing hip replacement")
To begin the operation, the hip replacement surgeon will make incisions on either the back (posterior) or front (anterior) of the hip. Both approaches offer pain relief and improvement in walking and movement within weeks of surgery.
How should I prepare for hip replacement surgery?
There are certain steps patients can take both before and after surgery to improve recovery time and results. It is important to follow the instructions and guidance provided by your orthopedic surgeon, medical team and rehabilitation therapist. Visit Preparing for Your Surgery to get information on preoperative hip replacement classes and patient education materials about joint replacement surgery.
Can hip replacement be done as an outpatient?
Most patients will stay in the hospital one or two nights after surgery. Some patients may be able to have same-day hip replacement and return home after an outpatient procedure.
How long does hip replacement surgery take?
Total hip replacement surgery takes about one and a half hours. Most patients also stay in the hospital for one or two days after the procedure.
What is hip replacement surgery recovery like?
Your rehabilitation will begin within 24 hours after surgery. Most hip replacement patients progress to walking with a cane, walker or crutches within a day or two after surgery. As the days progress, you will increase the distance and frequency of walking.
If you have THR surgery:
- Your recovery will begin directly following surgery in the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU), where your medical team will manage your pain and monitor your vital signs.
- Once the anesthesiologist is satisfied with your condition, you will be moved to an inpatient recovery room to monitor your progress.
- You will most likely have a dressing and tube on your hip for drainage, which should be removed the day after surgery.
- The pain management team will assess your medication and use a multifaceted approach to ensure comfort and mobility during the rehabilitation process.
- You will begin rehabilitation with a physical therapist within 24 hours. Your therapist will help you sit up, get in and out of bed, and practice walking and climbing stairs using a walker, cane or sometimes crutches.
- You will then continue physical therapy outside the hospital for 6 to 8 weeks. After that period, most patients are able to do everyday activities and return to playing sports.
Can I have both hips replaced at the same time?
Yes, healthy patients younger than 75 years old who have no history of cardiopulmonary disease may be able to have both hips replaced at once. In some cases, however, it may be better to stage the surgeries.

